[ICCP 2022] HiddenPose: Non-Line-of-Sight 3D Human Pose Estimation
Abstract:
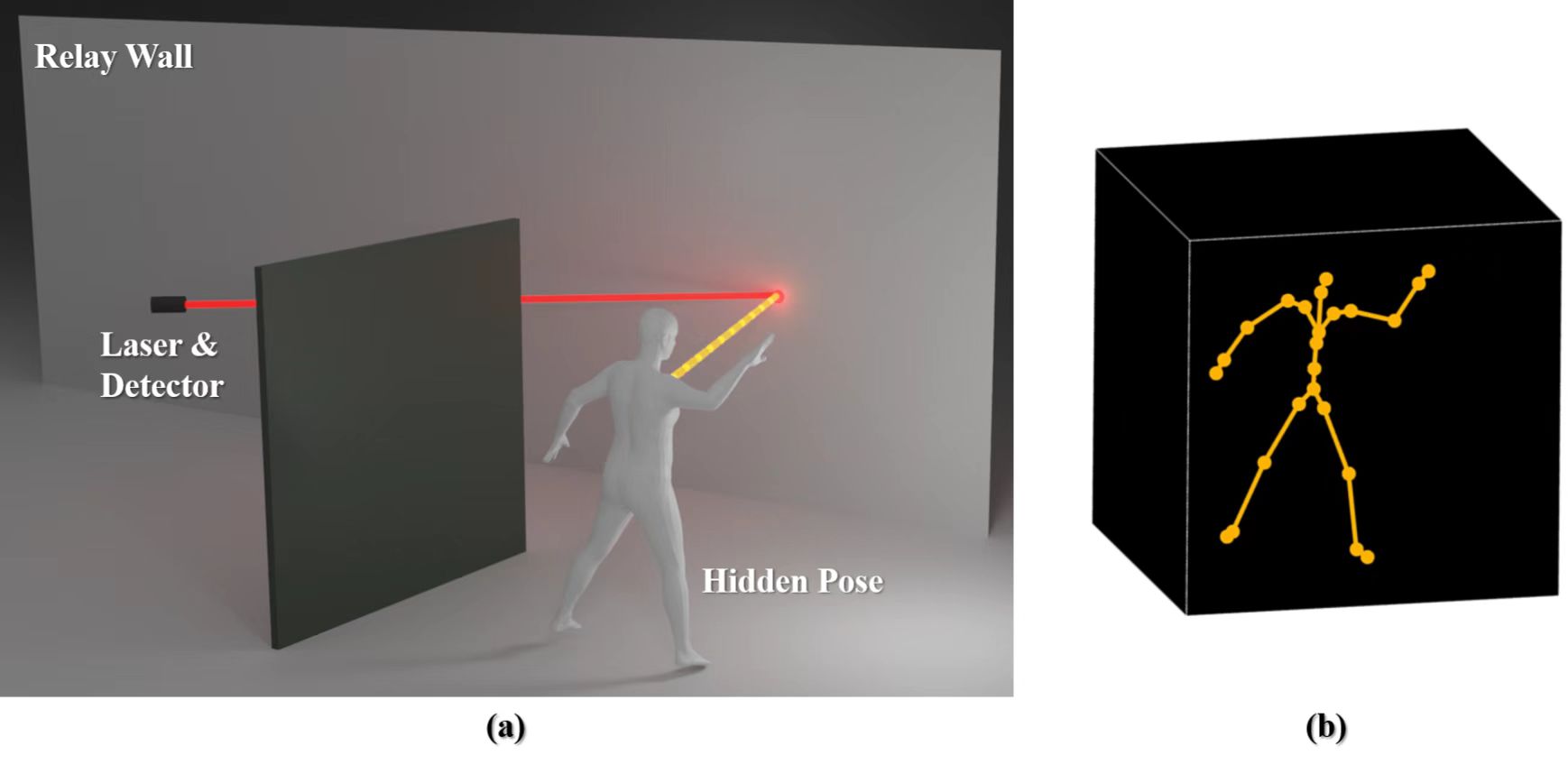
Nearly all existing human pose estimation techniques address the problem under the line-of-sight (LOS) setting. Many real-life applications such as rescue missions and autonomous driving, in contrast, require estimating the pose of hidden subjects. In this paper, we present a non-line-of-sight (NLOS) pose estimator, which produces a skeletal representation of hidden human poses. A brute-force approach would first conduct albedo reconstruction of a hidden subject and then apply LOS pose estimation. We show that such an implementation does not effectively exploit features unique to NLOS and subsequently yields artifacts such as missing joints. We instead first generate a comprehensive NLOS human pose dataset of 19 subjects under 9 motions. We then present a spatially aware deep learning technique based on convolutional neural networks that explicitly employ NLOS features. Comprehensive experiments on both synthetic and real data show that our new estimator is both effective and robust and can be seamlessly integrated into learning-based NLOS scene reconstruction. Our HiddenPose transient dataset contains synthetic transients with ground-truths of the volumes and the joints and real-world transients captured from our NLOS imaging system. Extensive assessments demonstrate that the HiddenPose transient dataset is valuable for effective NLOS research. We will make our data and code publicly available.
Non-line-of-sight Imaging
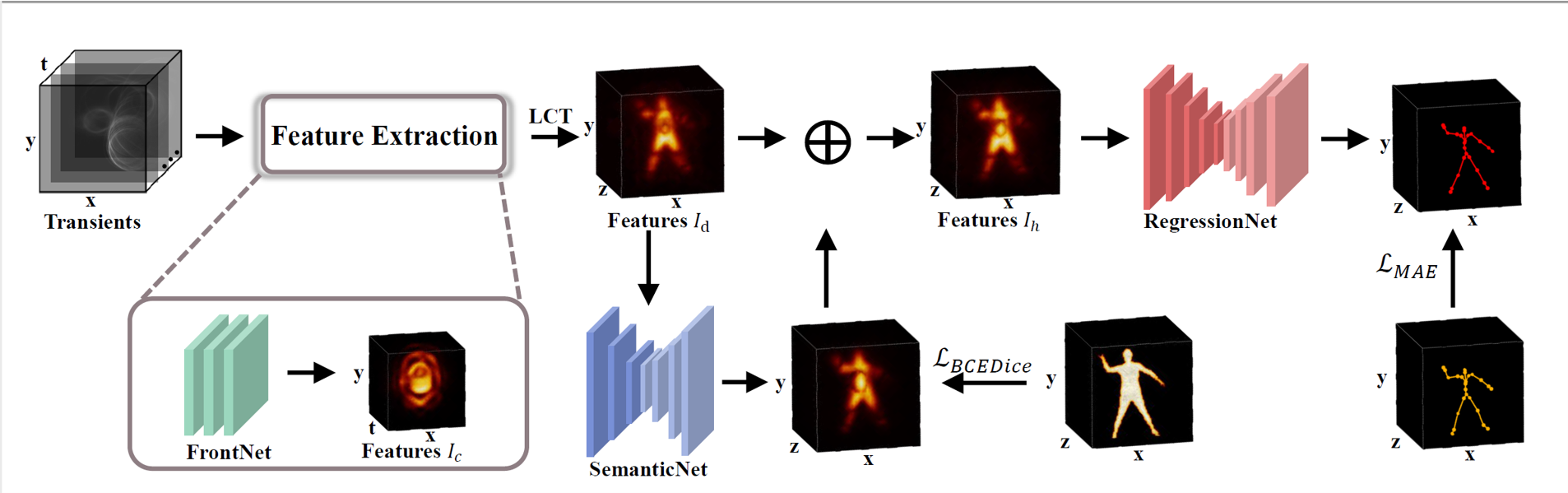
HiddenPose Estimator
We propose a HiddenPose estimator to predict 3D joints of a hidden human pose. The key ideas of our estimator are to transform the transients $\tau \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N \times T}$ into 3D spatial features $I_d \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N \times L}$ and to generate complete 3D features of the hidden human pose. $M \times N$ represents the spatial resolution, $T$ the time bins, and $L$ the distance between the hidden pose and the relay wall. Specifically, we consider that noise in the transients is irrelevant to the human body and apply a shallow 3D CNN-based FrontNet to extract local spatial-temporal features $I_c$ from the input transients $\tau$. $I_c$ preserves intrinsic spatial-temporal features of the transients while suppressing the noise. We then apply the LCT method to transform $I_c$ into 3D spatial features $I_d$, which contain the shape and albedo of the front surface but lack information about inner and back surface of the human body.
We then tailor a CNN-based network guided by semantic information, i.e., SemanticNet, to refine the 3D features that represent the possibility of the 3D volume of the human body.
Following the architecture of 3D ResNet , we implement a RegressionNet using CNN-based residual connections as the backbone to encode the voxel-wise features $I_{h}$. The decoder consists of four-layer 3D deconvolution to output a 3D likelihood heatmap for each joint of the human pose. Using these 3D heatmaps, we estimate the positions of human joints.
HiddenPose Transient Dataset
We provide a HiddenPose transient dataset for NLOS research on, e.g., NLOS reconstruction, human pose estimation, and activity recognition. Our dataset contains synthetic transients of more than 40k single-shot human poses, which are rendered using our synthesis scheme, and real-world transients of six single-shot human poses captured from our NLOS imaging system.
The code is available at Code Release.